T-Mobile recently launched at least two ads which make an interesting snapshot of how the mainstream views kink.
Brownmiller’s statement probably had a lot to do with the anti-SM strain of feminism in the late 1970s and early 1980s. In her view, masochism is merely a myth of patriarchy, an excuse for rape.
Brown, Carolyn E. “Erotic Religious Flagellation and Shakespeare’s Measure for Measure”, English Literary Renaissance, Vol.16, Iss. 1, Dec 1986
Shakespeare’s play Measure for Measure (first performed in 1604) links religious asceticism and flagellation with deviant sexuality and political tyranny. The Duke of Vienna, the judge Angelo and the novice nun Isabella claim to be pious and chaste, while their sexuality is repressed in such a way that it emerges as indifferent voyeurism, aggressive sadism or masochism, respectively. “…by drawing parallels to historical or topical events, Shakespeare suggests that the protagonists’ very asceticism, ironically, causes this deviant desire and that they associate their austere religious practices with pleasurable feelings.”

Isabella and Angelo
The plot revolves around a couple, Claudio and Juliet, who have not properly observed all the rules of engagement and marriage. While the Duke travels through Vienna in disguise as a friar, he hands power over to the judge Angelo, who decides to make an example of Claudio and condemn him to death for fornication. Claudio’s friend Lucia asks Isabella, the novice nun and Claudio’s sister, for help. Angelo offers to free Claudio in exchange for sex with Isabella.
The trio of the Duke, Angelo and Isabella are all ascetics (though none are actually clergy), and are hostile to sexual desires, believing that “pain kills the libido and thus subjecting themselves and others to physical abuse.”
On Thursday, October 17th, 7pm, I am presenting at the Vancouver’s Arts Club Theatre’s production of Venus in Fur, a two-hand play by David Ives.
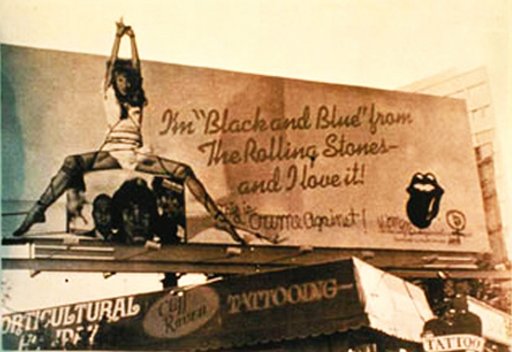
Erosblog has the story on the billboard advertisement for the Rolling Stones’ Black and Blue album (1976), featuring model Anita Russell in bondage (allegedly tied by Mick Jagger himself).
In researching the history of consensual sadomasochism, there isn’t a comprehensive body of knowledge to draw upon, no established canon of reference works, no Journal of Sadomasochistic Studies.
Instead, I have data points: case studies, books (often anonymous), anecdotes, images, etc. I’ll admit that sometimes what is and isn’t a data point is decided on the “I know it when I see it” principle. Connecting those points requires a certain amount of guesswork and judgment calls.
For example: Dr. Samuel Johnson, English man of letters of the Enlightenment, and his relationship with his close friend Hester Thrale. The latter’s posthumous effects, sold at auction in 1823, included a padlock and fetters. Thrale identified it as “Johnson’s padlock, committed to my care in the year 1768.” In 1767 or 1768, Thrale wrote that “our stern philosopher Johnson trusted me… with a secret far dearer to him than his life”. On other occasions , she wrote that “this great, this formidable Doctor Johnson kissed my hand, ay & my foot too upon his knees!” and quoted him saying, “a woman has such power between the ages of twenty five and forty five, that she may tie a man to a post and whip him if she will.” Finally, there is a reference in Thrale’s journal to “the fetters & padlocks [that] will tell posterity the truth”, and Johnson’s own journal entry, dated 24 March 1771, about “Insane thoughts on fetters and hand-cuffs.” (in Latin) (Pg.387-388)
Baatz, Simon. For the Thrill of It: Leopold, Loeb, and the Murder that Shocked Chicago. HarperCollins, 2008 Amazon
I wish there were more case studies to examine in this field. It’s rare to find a documented sadomasochistic relationship in the pre-modern era; I shudder to think how easily the Munby-Cullwick papers could have been lost. Sometimes one must make do with what one can find. In this case, there’s the case of Nathan Leopold and Richard Loeb who probably would have been remembered as eccentrics if they hadn’t kidnapped and murdered a teenage boy, basically just to prove they could.
After their capture for the murder, the two men were thoroughly examined by physicians, neurologists and psychiatrists, who couldn’t agree on a diagnosis. Eventually they were found competent to stand trial. Their examinations and testimonies revealed both had vivid fantasy lives.
Salon.com has an interview with former nun Mary Johnson, who worked under Mother Theresa at her mission in India. Currently being considered for canonization, the late Mother Theresa has come under scrutiny for her beliefs in the nobility in suffering, not only the voluntary kind, which border on religious masochism.
During your time with the sisters, you gave up all possessions—your hair, which had to be shorn every month, an audiotape sent by your parents, even photographs. How does this relate to the fusion of love and pain?
The Missionaries of Charity set out to live like the poor they serve. We each had two sets of clothes, which we’d wash by hand every day in buckets. We ate rotting vegetables and stale bread that we’d begged from wholesale grocers. We slept in common dormitories, without any privacy, on thin mattresses we’d made ourselves. Living poorly day by day convinces you that life is hard. For a Missionary of Charity, ideal love was self-sacrificing, even to the practice of corporal penance.
Your first session of self-flagellation is imprinted in my mind: “My knees shook. I took the bunch of knotted cords into my hands. From Sister Jeanne’s stall, I heard the beating sounds, one, two, three. . . . I swung harder. The skin of my lower thighs turned red, then red with white streaks as I hit harder.”
When I took that rope whip into my hands, I was scared, I was excited, I hoped that I was on my way to conquering my selfishness and becoming a holy person. When you visit the homes and shrines of various saints, you often see hair shirts or whips or spiked chains on display. This is a religion in which nearly every house of worship, classroom, and private home has as its most prominent feature the image of a bloodied, tortured man. We were taught that wearing spiked chains and beating ourselves allowed us to share in his work of redemption. I know it doesn’t make much sense when you say it just like that, but within that entire system it had its own weird logic.
I’m reminded of Hannah Cullwick and her nun-like devotion to her labours, based on her own private value system. Is this masochism? Of a kind.
The problem with this kind of thinking is what happens when you are in a position to impose it upon others, who have no choice in their conditions. Subsequent investigations have shown that her mission provided a standard of care that would be intolerable in any non-religious institution, and she avoided modern medicine. She followed a medieval line of thought that the soul in the afterlife was all that mattered, not the body in the moral world.
From Žižek’s “Organs without Bodies – Gilles Deleuze”:
And one finds a similar obscene subtext even where one would not expect it – in some texts which are commonly perceived as feminist. In order to confront this obscene “plague of fantasies” which persists at the level of “subliminal reality” at its most radical, suffice it to (re)read Margaret Atwood’s The Handmaid’s Tale, the distopia about the “Republic of Gilead,” a new state on the East Coast of the US which emerged when the Moral Majority took over. The ambiguity of the novel is radical: its “official” aim is, of course, to present as actually realized the darkest conservative tendencies in order to warn us about the threats of Christian fundamentalism – the evoked vision is expected to give rise to horror in us. However, what strikes the eye is the utter fascination with this imagined universe and its invented rules. Fertile woman are allocated to those privileged members of the new nomenklatura whose wives cannot bear children – forbidden to read, deprived of their names (they are called after the man to whom they belong: the heroine is Offred – “of Fred”), they serve as receptacles of insemination. The more we read the novel, the more it becomes clear that the fantasy we are reading is not that of the Moral Majority, but that of feminist liberalism itself: an exact mirror-image of the fantasies about the sexual degeneration in our megalopolises which haunts members of the Moral Majority. So, what the novel displays is desire – not of the Moral Majority, but the hidden desire of feminist liberalism itself.
So, it’s not just fantasies that reflect reality, but fantasies that reflect each other. Moral Majority types have their dystopian fantasies of women stolen away by dark Others, and fantasize utopias of patriarchal order. Liberal feminists have their dystopian fantasies of the world the Moral Majority would create, a masochistic fantasy of defeat and vindication.
From Tanos’ blog:
…Lush, the high street retailer of bath bombs etc, ran a campaign in many of their shop windows involving people in cages or dressed as animals to highlight animal testing of cosmetics. In their Regent Street shop they put on a performance lasting several hours in which a body-stocking naked actress was tortured by a man in a white coat. Not surprisingly, the coverage of this got some BDSM attention.

